概述
- 类名:ApplicationContextInitializer
- 介绍:Spring容器刷新之前执行的一个回调函数
- 作用:向SpringBoot容器中注册属性
- 使用:继承接口自定义实现
// 可以指定@Order(XX)
public class MyInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> {
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext configurableApplicationContext) {
// TODO:初始化逻辑实现
}
}
实现方式
- 都要实现ApplicationContextInitializer接口;@Order值越小越先执行;application.properties中定义的优先于其它方式。
- 实现方式一:
- 实现ApplicationContextInitializer接口。
- SpringApplication类初始化后设置进去。
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(MyApplication.class);
application.addInitializers(new MyInitializer());
application.run(args);
}
}
- 实现方式二:(推荐)
- 实现ApplicationContextInitializer接口。
- spring.factories内填写接口实现。
- key值为org.springframework.contet.ApplicationContextInitializer。
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=com.wzl.springboot.initializer.MyInitializer
- 实现方式三:
- 实现ApplicationContextInitializer接口。
- application.properties内填写接口实现。
- key值为context.initializer.classes
context.initializer.classes=com.wzl.springboot.initializer.MyInitializer
SpringFactoriesLoader
- 用途:SpringFactoriesLoader类的主要作用是通过类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories文件获取工厂类接口的实现类,初始化并保存在缓存中,以供Springboot启动过程中各个阶段的调用。
- 要点:
- 框架内部使用通用工厂加载机制
- 从classpath下多个jar包特定的位置读取文件并初始化类
- 文件内容必须是kv形式,即properties类型
- key是全限定名(抽象类|接口)、value是实现,多个实现用逗号分隔
- 作用:
- 从类路径jar包中读取特定文件实现扩展类的载入
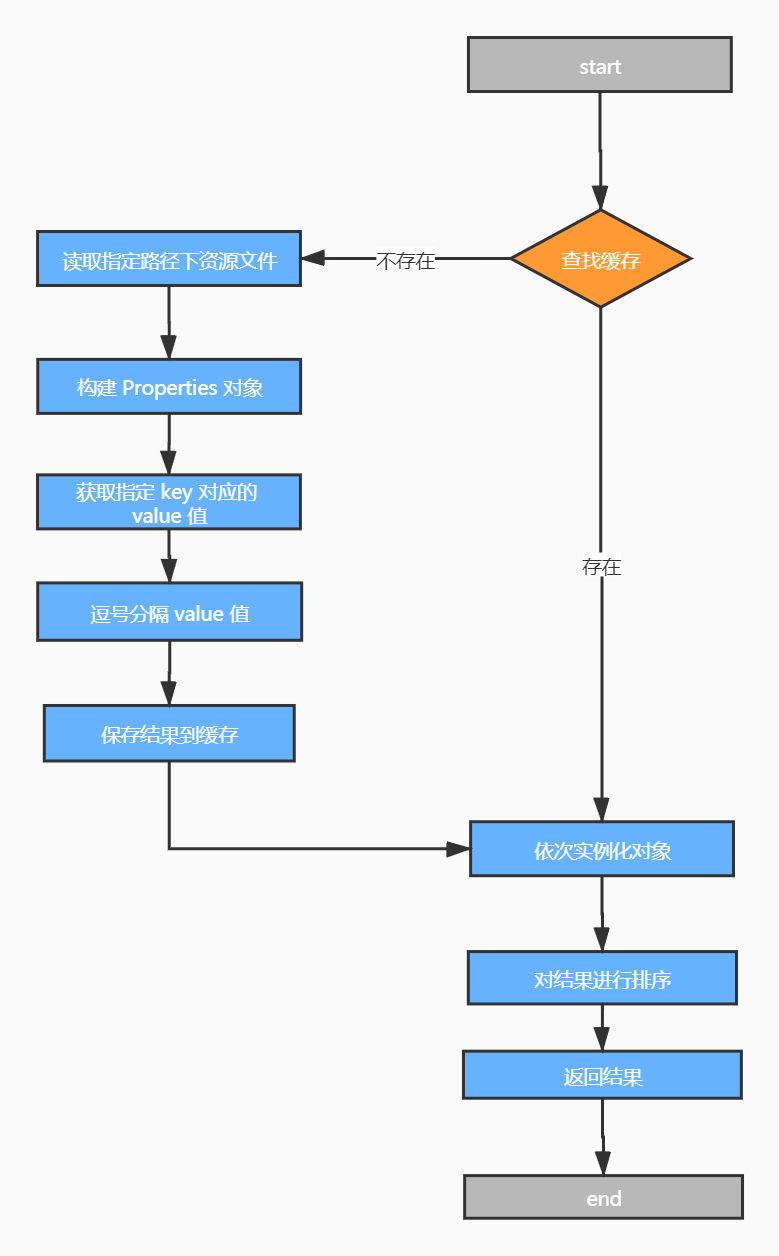
- loadFactories流程:
- 查找缓存
- 读取指定资源文件
- 构造properties对象
- 获取指定key对应的value值
- 逗号分割value
- 保存结果到缓存
- 依次实例化结果对象
- 对结果对象排序
- 返回结果
- spring.factories:设置目的是帮助spring-boot项目包以外的bean(即在pom文件中添加依赖中的bean)注册到spring-boot项目的spring容器中。由于@ComponentScan注解只能扫描spring-boot项目包内的bean并注册到spring容器中,因此需要@EnableAutoConfiguration注解来注册项目包外的bean。而spring.factories文件,则是用来记录项目包外需要注册的bean类名。
成员变量
// 指定spring.factories的文件路径
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
// 使用基于common-logging的运行方式记录日志
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(SpringFactoriesLoader.class);
// MultiValueMap<String, String>> 表示这个ClassLoader加载器加载的类的集合
private static final Map<ClassLoader, MultiValueMap<String, String>> cache = new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>();
loadFactories()
- 用途:使用给定的类加载器,从FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION加载并实例化给定类型的工厂实现。
- 在返回工厂之前,都会通过AnnotationAwareOrderComparator这个类来进行排序。
- 如果需要自定义实例化策略,要使用loadFactoryNames()去获取所有注册的工厂名称。
// factoryType代表工厂的接口或抽象类,classLoader是默认为空的类加载器
public static <T> List<T> loadFactories(Class<T> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(factoryType, "'factoryType' must not be null");
// 类加载器
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
// 如果为空则用系统默认类加载器
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
// 获取所有工厂实现类的名称集合
List<String> factoryImplementationNames = loadFactoryNames(factoryType, classLoaderToUse);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded [" + factoryType.getName() + "] names: " + factoryImplementationNames);
}
List<T> result = new ArrayList<>(factoryImplementationNames.size());
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
// 实例化工厂实现类,然后添加进result集合中
result.add(instantiateFactory(factoryImplementationName, factoryType, classLoaderToUse));
}
// 通过AnnotationAwareOrderComparator#sort方法对工厂名称进行排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(result);
return result;
}
loadFactoryNames()
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 获取到factoryType工厂类型
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
// 加载SpringFactories,如果没有则返回一个空集合
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
loadSpringFactories()
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
// 从缓存中获取已经加载过的SpringFactories
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
// / 通过类加载器读取类路径下的spring.factories文件,然后封装成URL存储于Enumeration中
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
// 遍历urls,再将url封装成UrlResource对象
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
/**
* 通过PropertiesLoaderUtils属性加载器去加载spring.factories中的value值。
* 这里的Properties是继承了HashTable的一个属性,key和value就对应着spring.factories文件里的key和value。
* 在PropertiesLoaderUtils中,底层是通过IO流读取的文件数据,这里就不细说了。
*/
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
// 遍历获取工厂实现类名称
for (String factoryImplementationName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) {
result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
// 将获取结果存入缓存中
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
instantiateFactory()
// factoryImplementationName是工厂实现类的名称
private static <T> T instantiateFactory(String factoryImplementationName, Class<T> factoryType, ClassLoader classLoader) {
try {
// 通过classUtils工具类获取工厂实现类的Class对象
Class<?> factoryImplementationClass = ClassUtils.forName(factoryImplementationName, classLoader);
// 异常处理
if (!factoryType.isAssignableFrom(factoryImplementationClass)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Class [" + factoryImplementationName + "] is not assignable to factory type [" + factoryType.getName() + "]");
}
// 通过反射工具创建工厂类实例对象
return (T) ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(factoryImplementationClass).newInstance();
}
// 异常处理
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Unable to instantiate factory class [" + factoryImplementationName + "] for factory type [" + factoryType.getName() + "]",ex);
}
}
系统初始化器
- 作用:
- 上下文刷新即refresh方法前调用。
- 用来编码设置一些属性变量,通常用在web环境中。
- 可以通过order接口进行排序
applyInitializers()
// 注册初始化器
protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 遍历并获得初始化器
for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : getInitializers()) {
// 判断初始化器的泛型是否为ConfigurableApplicationContext
Class<?> requiredType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializer.getClass(), ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
Assert.isInstanceOf(requiredType, context, "Unable to call initializer.");
// 调用初始化器的initialize方法
initializer.initialize(context);
}
}
getInitializerClass()
- SpringBoot在加载系统初始化器时会先加载 DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer类,因为它的order是0。而它所做的事情就是去加载context.initializer.classes下面的实现类。
- 因此application.properties中定义的优先于其它方式。
private List<Class<?>> getInitializerClasses(ConfigurableEnvironment env) {
String classNames = env.getProperty("context.initializer.classes");
List<Class<?>> classes = new ArrayList();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(classNames)) {
String[] var4 = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(classNames, ",");
int var5 = var4.length;
for(int var6 = 0; var6 < var5; ++var6) {
String className = var4[var6];
classes.add(this.getInitializerClass(className));
}
}
return classes;
}
